From Ideas to Innovation: How Design Thinking Can Drive Business Success
“Apple’s success with the iPod and iPhone is often attributed to its use of design thinking. By focusing on the user experience and creating products that are easy to use and aesthetically pleasing, Apple was able to create highly successful products in the marketplace.
Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that places empathy for the user at the center of the process. It is a methodology that originated in the design world but has been embraced by businesses of all sizes and industries.?
At its core, design thinking is about understanding the people who use your products or services and designing solutions that meet their needs. It is a human-centered approach that prioritizes collaboration, experimentation, and iteration.?
By embracing design thinking, companies can create products and services that are more user-friendly, innovative, and profitable.
Design Thinking Elements
Design thinking is a non-linear process that involves six elements: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, Test, and Implement.
1. Empathize: The first element of the design thinking process involves understanding the needs and perspectives of the user. This involves gathering insights by observing, listening, and empathizing with the user to identify their needs and challenges.
2. Define: The next element involves synthesizing the insights from the empathize phase to define the problem statement. This consists in reframing the problem statement to align with the user’s needs, goals, and desires.
3. Ideate: The ideation element is where the brainstorming process takes place. This is where you generate a range of creative ideas and solutions that will help address the defined problem. At this stage, every idea is correct, and the aim is to encourage creativity and generate as many ideas as possible.
4. Prototype: Once you have a set of potential ideas and solutions, the next step is to prototype them. This involves creating low-fidelity prototypes of the most promising ideas and testing them with the users. The aim is to gather feedback and insights to help refine and iterate on the prototypes.
5. Test: This element of the design thinking process tests the prototypes with the user to validate the solutions. Testing is where the solution gets tested by users in their real-life settings. During testing, the ultimate user experiences the prototype without explicit guidance to observe how users react to a product and listen to their feedback on different aspects. Testing helps determine the solution’s feasibility, viability, and desirability.
6. Implement: This is the last element in the design thinking process. At this point, all observations, ideas, and developments are put into practice by creating a solution. This is when the solution is finally launched and tested in the market, making it a reality. However, not all designs make it to this stage. It is possible that the solution did not meet the user’s needs as intended, resulting in the need to return to the ideation stage and revising the idea.
It is important to note that design thinking is an iterative process in which product or user experience designers look to understand the user better, leave their assumptions behind and uncover alternative solutions that may only be visible later. Understanding that each process element can inform the other elements is important. For example, when going through user testing, you may learn about a new problem that didn’t come up during the previous elements.
Tools and Techniques for Design Thinking
There are many tools and techniques for design thinking. These tools and techniques encourage creativity, experimentation, and collaboration and can help businesses develop innovative solutions.
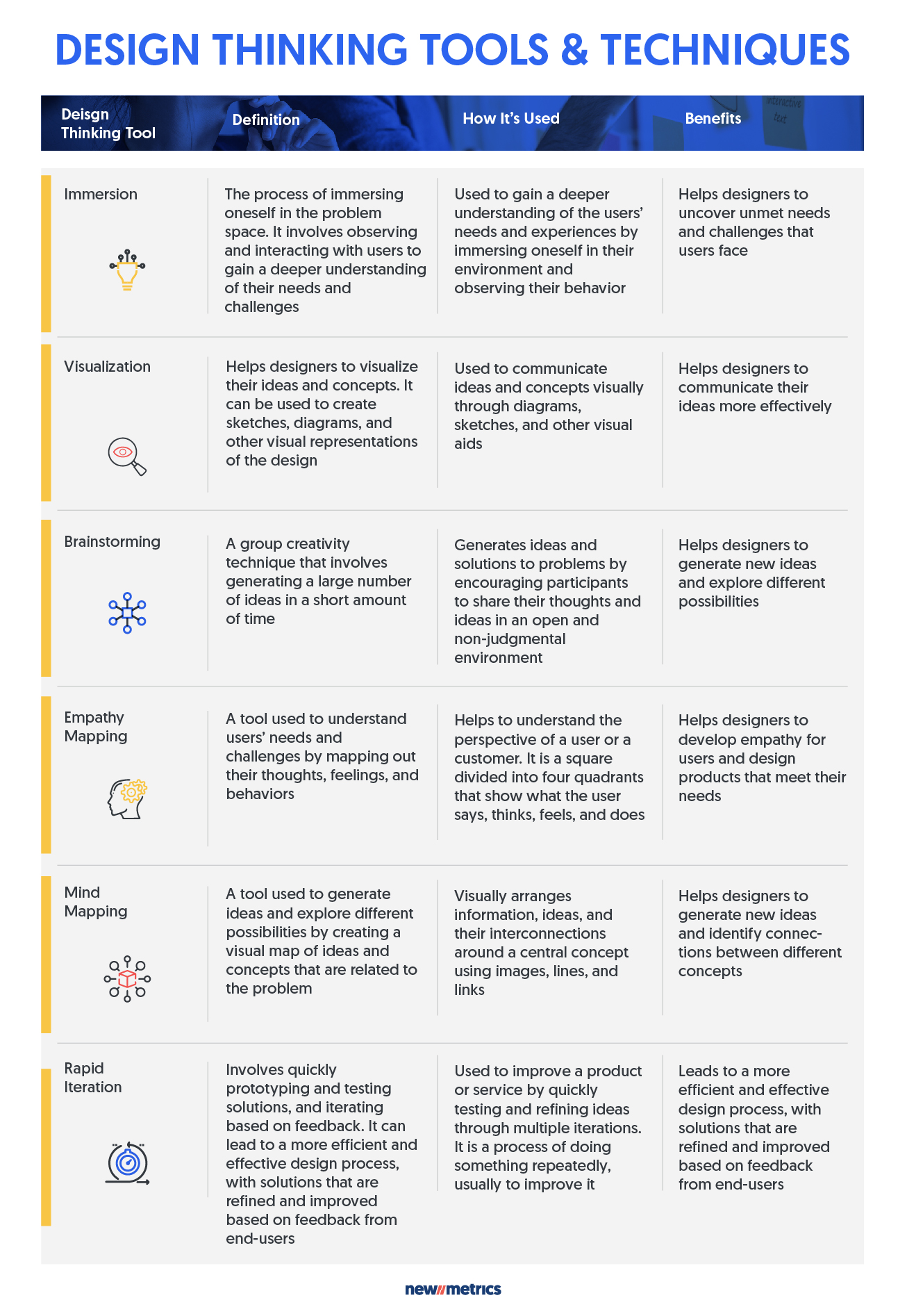
- Immersion: This is the process of immersing oneself in the problem space. It involves observing and interacting with users to better understand their needs and challenges.
- Visualization: This tool helps designers to visualize their ideas and concepts. It can be used to create sketches, diagrams, and other visual representations of the design.
- Brainstorming: This technique is used to generate a large number of ideas in a short amount of time. It involves a group of people coming together to share and build on each other’s ideas.
- Empathy Mapping: This technique helps you understand your customers’ needs and emotions. It involves creating a visual map of your customer’s experience, including what they think, feel, see, hear, and do.
- Journey Mapping: Similar to empathy mapping, journey mapping involves visually mapping out a customer’s experience with your business. However, journey mapping includes a more detailed breakdown of each step in the process.
- Mind Mapping: This technique helps you brainstorm and organize ideas. It involves starting with a central idea and then branching into related ideas.
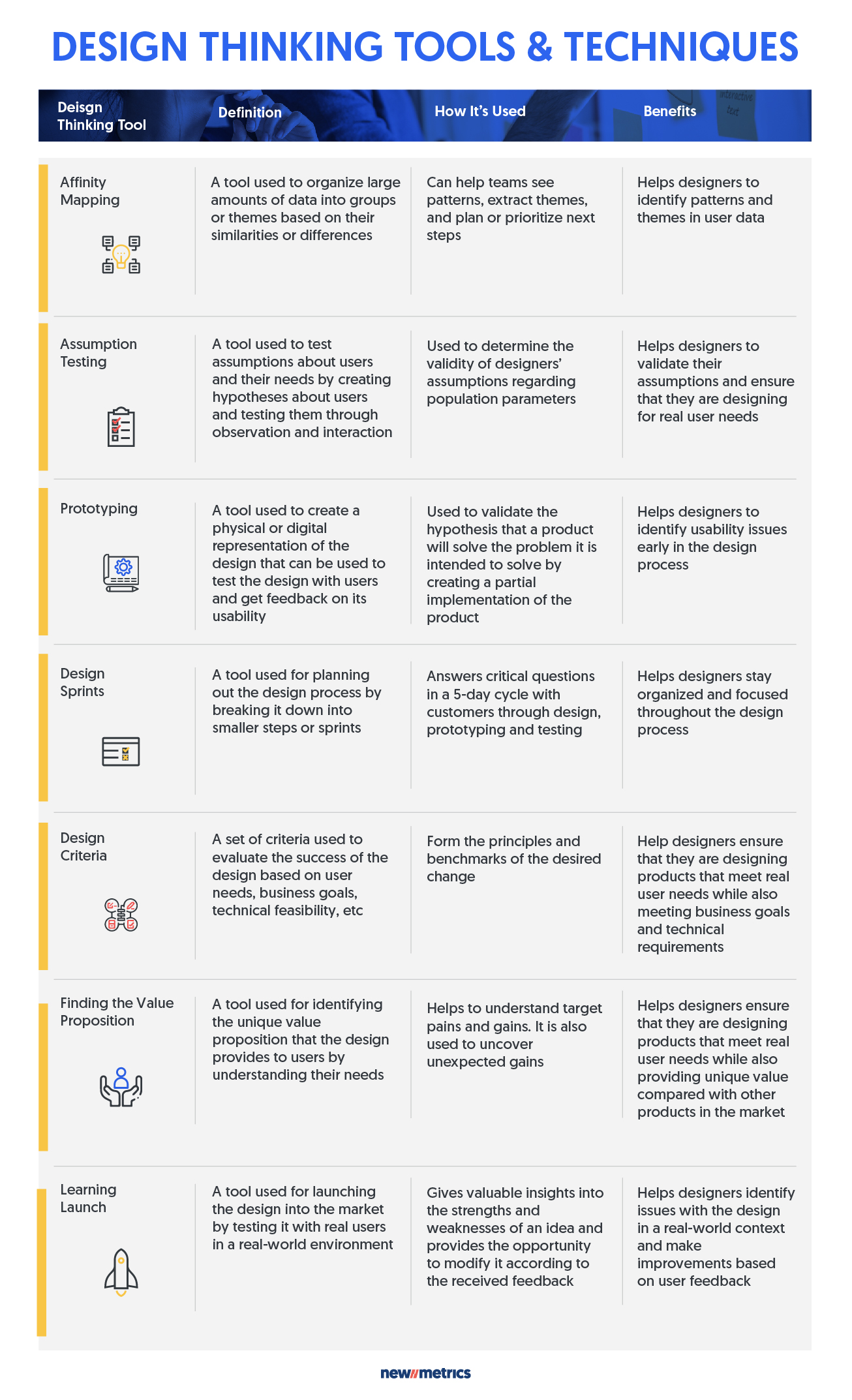
- Affinity Mapping: A technique used to group ideas into categories. It involves writing each idea on a sticky note and then grouping the sticky notes into categories.
- Rapid Iteration: This tool involves quickly prototyping and testing solutions and iterating based on feedback. It can lead to a more efficient and effective design process, with refined and improved solutions based on end-user feedback.
- Assumption Testing: This tool tests assumptions about users and their needs. It involves creating hypotheses about users and testing them through observation and interaction.
- Prototyping: This tool creates a physical or digital representation of the design. It can be used to test the design with users and get feedback on its usability.
- Design Sprints: This time-constrained process involves a team coming together to work on a specific problem or challenge. It typically involves five stages: understand, diverge, converge, prototype, and test.
- Design Criteria: Involve establishing criteria or principles you want your product or service to meet. It can help guide the design process and ensure the result meets your desired goals.
- Finding the Value Proposition: This tool identifies the unique value the design provides to users. It involves understanding users’ needs and how the design meets those needs.
- Learning Launch: This tool is used to launch the design into the market. It involves testing the design with real users in a real-world environment.
These tools and techniques can be used individually or in combination to help guide the design thinking process in a business.
Design Thinking Methodology
The Double Diamond design thinking model is a framework for innovation and creativity developed by the British Design Council. It consists of four steps that alternate between divergent and convergent thinking, from exploring the problem space to delivering the solution space. The steps are Discover, Define, Develop, and Deliver, and each one can use different tools and methods.
The first diamond represents exploring an issue more widely or deeply (divergent thinking), and the double diamond represents converging on a specific solution (convergent thinking). The first diamond is about discovering the problem space and exploring all possible solutions. The second diamond defines the problem space and develops a specific solution.
Here are some examples of tools and methods used in each step of the Double Diamond design thinking model:
- Discover: This phase is about understanding the issue rather than merely assuming it. It involves speaking to and spending time with people affected by the problem. Some tools and methods used in this phase include user research, interviews, surveys, and observation.
- Define: This phase defines the problem space and develops a specific solution. Some tools and methods used in this phase include persona development, empathy mapping, problem framing, and journey mapping.
- Develop: This phase is about exploring all possible solutions. Some tools and methods used in this phase include brainstorming, mind mapping, prototyping, and testing.
- Deliver: This phase is about delivering the solution space. Some tools and methods used in this phase include user testing, feedback loops, and iteration.
Benefits of Using Design Thinking in Business
Design thinking is a method for solving complex problems, using the creative strategies initially used to design a new product. It helps organizations identify opportunities, unlock innovation, and improve their businesses. Understanding design thinking and applying it on an organizational level as a tool for transformation can create radical changes in your business and help you become an industry pioneer. By putting human needs at the center of the problem-solving process, design thinking offers numerous benefits that can lead to business success.
Here are some of the key benefits of design thinking:
• Improved customer experiences: Design thinking involves empathy and understanding the user’s needs, pain points, and challenges. By focusing on user-centered design, companies can develop products and services that resonate with their customers, leading to more successful launches, positive reviews, and repeat business.
• Increased customer loyalty and retention: Design thinking helps create great products and services and fosters more profound connections between companies and their customers. Businesses can build loyalty and drive repeat business by delivering solutions that meet customer needs and desires.
• Faster innovation cycles: The design thinking process encourages rapid prototyping, testing, and iteration. This approach leads to quicker product development, shorter innovation cycles, and more successful outcomes.
• Cognitive flexibility: Design thinking can help overcome cognitive fixedness by encouraging employees to approach problems with an open mind and a willingness to explore new ideas. By emphasizing empathy and observation, employees can better understand the problem they are trying to solve and the needs of their customers.
Design thinking also involves ideation, which is the process of generating a large number of ideas. By generating a large number of ideas, a designer can explore a wide range of possibilities and avoid getting stuck on a single idea.
Finally, design thinking involves prototyping and testing solutions with customers. This allows designers to get feedback on their ideas and make improvements based on that feedback. By testing their ideas with customers, designers can avoid getting stuck on a single solution and develop solutions tailored to the customer’s needs.
• Greater team collaboration: Design thinking is a collaborative process that requires teams from diverse backgrounds and disciplines to work together to solve complex problems. This fosters better communication, teamwork, and cross-functional understanding, leading to a more efficient and productive workforce.
• User-centered approach to problem-solving: By understanding users’ and stakeholders’ needs, wants, and behaviors, businesses can effectively develop solutions that meet their needs. This approach can lead to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
• Prototypes and testing development: Design thinking also involves prototyping and testing solutions with customers. This allows designers to get feedback on their ideas and make improvements based on that feedback. By involving customers in the design process, designers can ensure that their solutions meet the customer’s needs. Businesses can identify and address potential issues early on by testing and refining solutions before implementing them, saving time and resources.
• Reduced risk and cost: By testing prototypes and ideas earlier in the design process, companies can minimize risks and avoid costly mistakes. Design thinking also helps teams identify problems and find solutions earlier in the development cycle, reducing costs and time-to-market.
Design thinking can offer a range of benefits for businesses looking to drive innovation and solve complex problems. By focusing on customer needs, collaborating across teams, and iterating quickly, companies can deliver more successful outcomes, build customer loyalty, and drive business success.
How to Incorporate Design Thinking into Your Business
You must first understand the methodology and process to incorporate design thinking into your business. Design thinking training and workshops are available to help companies to understand and implement design thinking effectively.
Additionally, businesses can create a design thinking team or hire a design thinking consultant to guide the process. Involving all stakeholders in the design thinking process ensures everyone’s needs are considered.
Finally, creating a culture that encourages creativity, experimentation, and collaboration is essential. This culture should prioritize innovation and problem-solving and should be supported by leadership.
Here are some tips on how to incorporate design thinking into your business:
• Engage with empathy: Empathy is considered the starting point for any design project and constitutes phase one of the Design Thinking process. During the empathize phase of the Design Thinking process, you’ll need to both observe and engage with your users. Empathy is our ability to see the world through other people’s eyes – to understand their needs and desires. It helps you create better solutions that meet the end user’s needs and desires of your end users. It involves immersing oneself in the community and setting aside preconceived notions. Empathy puts people at the center of your design.
Incorporating empathy into design thinking helps designers create more user-friendly products that meet user needs more effectively. By understanding users’ needs and desires, designers can create products that are more intuitive and easier to use. Empathy also helps designers identify pain points in a user’s experience with a product or service.
• Take risks: Getting it wrong is vital to success because failure is not a step backward but an excellent stepping stone to success. The most progressive companies encourage employees to take risks and reward them for trying. We never learn to move out of our comfort zone if we don’t overcome our fear of failure. Failure can be a valuable learning experience that helps us grow and develop. It can help us identify areas to improve and develop new skills. By learning from our mistakes, we can become more resilient and better equipped to handle future challenges.
• Introduce Design Thinking into your company gradually: It’s essential to introduce progressively design thinking into your organization. Don’t try to convince your employees of Design Thinking’s merits immediately. Instead, introduce the concept slowly and let them see how it can benefit them. Start small and create small experiments that allow your team to practice gathering data, testing frequently, and iterating quickly. This will help you build momentum and get people excited about the possibilities of design thinking.
• Present the advantages of Design Thinking: Design thinking is a method for solving complex problems, using the creative strategies initially used to design a new product. It helps you go about things differently—not solving a problem the same way every time. Once you have a few good options, they need to be embraced by the group. In this final stage, a course of action is selected, and resources are allocated to achieve goals.
• Secure the support of your higher-ups: There are several ways to secure the support of higher-ups for design thinking:
- Leverage empathy, encourage divergence, and navigate ambiguity.
- Focus on human needs and behaviors and how to create a solution that matches those needs.
- Encourage collaboration and teamwork.
How Design Thinking Improves Business
Design thinking can help businesses in numerous ways. From ideation to problem-solving, the process encourages collaboration, innovation, and a customer-centric approach to all aspects of a business. Here are a few ways design thinking can be applied in business:
- Develop new products/services: Design thinking can help businesses create new products and services that better serve the needs of their customers. By understanding the customers’ needs and pain points, businesses can create solutions that make a difference in their lives.
- Redesign existing products/services: Businesses can use design thinking to improve their products and services. By empathizing with their customers, they can identify areas of improvement and make changes that increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Create a customer-focused culture: Businesses can shift their focus from internal processes to customer needs by adopting design thinking principles. This customer-centric approach can drive a culture of innovation, creativity, and continuous improvement.
- Solve business challenges: Design thinking can help businesses solve complex challenges by approaching problems from a different perspective. The process encourages creativity and collaboration, leading to unique solutions that might have yet to be discovered.
- Improve communication and collaboration: The design thinking process emphasizes collaboration, enabling businesses to break down silos and foster cross-functional teamwork. Companies can promote a culture of creativity and innovation by encouraging diverse perspectives and creating a safe space for open communication.
Design thinking is a human-centered approach to problem-solving that encourages creativity, experimentation, and collaboration. Design thinking encourages a user-centered approach to problem-solving and fosters innovation and experimentation.
Design thinking has proven valuable for businesses looking to innovate and stay ahead of the competition. By applying design thinking principles, businesses can create products and services that truly serve their customers’ needs, solve complex problems, and foster a culture of innovation and collaboration.